
How Does a Laser Tachometer Work in Modern Systems?
Share
In the dynamic field of technology, speed and precision are pivotal in various applications, particularly in industrial settings. One of the most fascinating innovations aiding in this endeavor is the **laser tachometer**. But **how does a laser tachometer work**? This article aims to delve deep into its operational mechanisms, applications, and advantages.
A **laser tachometer** is an advanced tool utilized primarily for measuring rotational speed with utmost accuracy. Its working principle hinges on the light emitted by a laser, which interacts with the rotating object to determine its speed by counting the number of revolutions over a specified time interval.
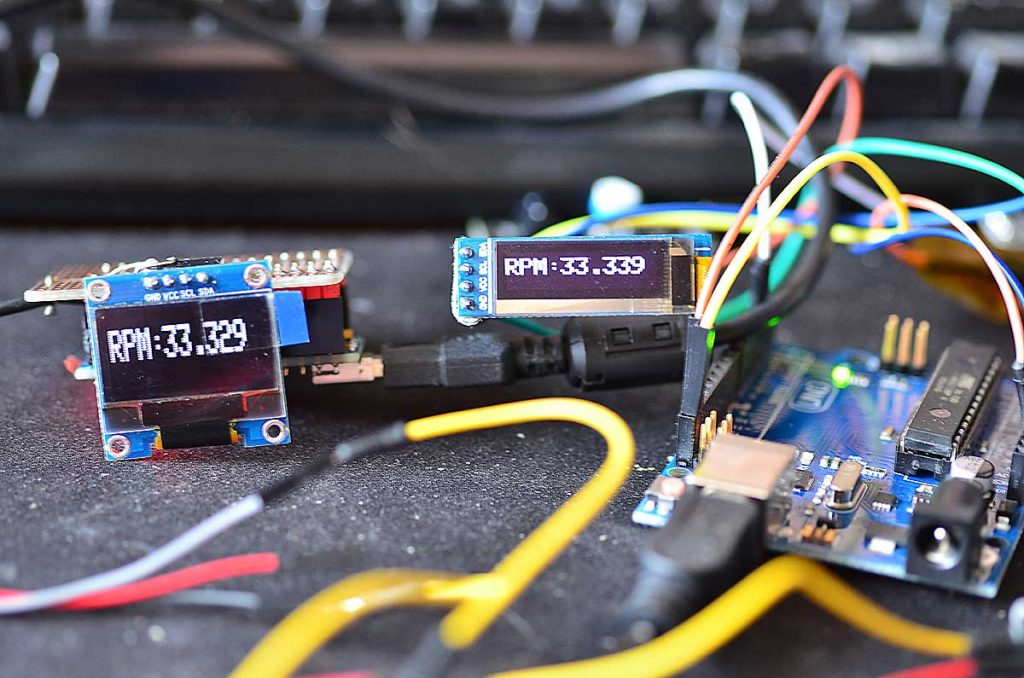
Understanding the Basics: What is a Tachometer?
Before we delve into the intricacies of laser tachometers, it is prudent to understand the **tachometer** itself. Essentially, a tachometer is an instrument that measures the rotational speed of an object, usually expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM). For a detailed exploration, check out this article on tachometers.
Working Principles of a Laser Tachometer
At its core, a **laser tachometer** works by the principle of **frequency measurement**. The laser emits a focused beam of light directed at a rotating object. As the object spins, the surface characteristics (like reflection or color) of the object modify **the reflected light** back to the sensor. This light is then detected by **photodetectors**, which analyze the return signals to compute the rotational speed.
The Process Explained
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how the process works:
- Laser Emission: The tachometer generates a laser beam aimed at the spinning object.
- Reflection: The rotating object reflects the beam back towards the sensor.
- Detection: The sensor detects the intensity and frequency of the reflected light.
- Calculation: The device applies formulae to compute the revolutions per minute based on changes in frequency due to the object's movements.
Advantages of Using Laser Tachometers
There are numerous benefits to employing **laser tachometers** over traditional methods. Some of these include:
- High Precision: The accuracy of laser measurement drastically reduces errors compared to mechanical or contact tachometers.
- Non-contact Measurement: Being a non-contact tool means it can measure speed without wear and tear on the machine or device.
- Versatility: Laser tachometers can be utilized across various industries including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Applications of Laser Tachometers
Laser tachometers find extensive applications across various sectors. They are frequently used in:
- Automotive Industries: For assessing engine RPM and timing adjustments.
- Manufacturing: To monitor speed in conveyor systems or manufacturing equipment.
- Aerospace: For evaluating rotational speed of parts in aircrafts, ensuring safety standards.
Comparison with Other Tachometers
When it comes to measuring rotational speed, several types of tachometers exist including analog, digital, and laser tachometers. Before opting for a tachometer, understanding the differences is vital. For insights on how to reset a tachometer, you can visit this guide.
Key Differences
The primary differences lie in their functionality and operational methods:
- Analog Tachometers: Typically use mechanical systems that contact the rotating object and can introduce errors due to friction.
- Digital Tachometers: Offer improved accuracy and can display numbers directly but may still require contact or proximity to the measured object.
- Laser Tachometers: Provide superior precision and operate without physical contact, eliminating potential wear and decreasing risk of machine damage.
How to Calibrate a Laser Tachometer
Calibration is a crucial aspect of ensuring accurate measurements. To properly calibrate a laser tachometer:
- Ensure the device is clean and free from obstructions.
- Point the laser towards a rotating object at a known speed.
- Adjust the readings on the tachometer until they match the known speed.
For a more comprehensive guide, visit this calibration guide.

Frequently Asked Questions
What types of applications are best suited for laser tachometers?
Laser tachometers are ideal for any application requiring precise speed measurements without physical contact, such as in manufacturing and automotive industries.
Can laser tachometers measure non-reflective surfaces?
Yes, they can measure non-reflective surfaces, although enhancing their reflectivity (e.g., using a reflective tape) can improve accuracy.
How do I know if my laser tachometer needs recalibration?
If you observe discrepancies in measurement or performance, it may indicate the need for recalibration.
For information on why a tachometer might not work, refer to this helpful resource. In conclusion, the **laser tachometer** is a groundbreaking instrument in speed measurement, providing a level of accuracy previously unattainable. As technology continues to advance, its applications will only expand, making it an essential tool across industries.
